Table of Content
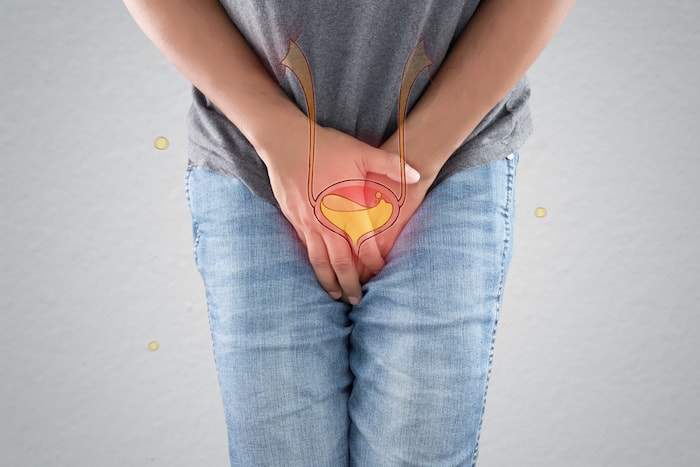
Discover causes of abdominal pain and frequent urination, including UTI, anxiety, and others. Frequent and urgent urination issues often occur together. You may feel the need to urinate often, and the urge comes on suddenly. Urgent urination describes an overwhelming need to get to a restroom immediately. It may be accompanied by pain or discomfort in the bladder or urinary tract. The key to deciding if you have issues with frequent urination is whether the need to urinate often is creating challenges in your life.

OAB happens when the nerves that tell your brain to empty your bladder don’t work right. The faulty signal causes the bladder muscles to contract and make you dash for the toilet. You have a sudden, urgent need to urinate many times during the day. When I was a truck driver I developed an urge to pee every time I saw a truck stop because that was "home". After menopause, women produce less estrogen, a hormone that helps keep the lining of the bladder and urethra healthy.
Why do we pee when we poop?
Deterioration of these tissues can aggravate incontinence. The rectum is located near the bladder and shares many of the same nerves. Hard, compacted stool in your rectum causes these nerves to be overactive and increase urinary frequency. Infections can irritate your bladder, causing you to have strong urges to urinate and, sometimes, incontinence. You experience frequent or constant dribbling of urine due to a bladder that doesn't empty completely. Behavioral therapy with or without biofeedback and pelvic floor electrical stimulation for persistent post-prostatectomy incontinence — a randomized controlled trial.
Sometimes called water pills, they’re often prescribed for high blood pressure. They help your body get rid of salt and water, so your bladder can fill up fast and may even leak. Once the underlying cause is treated, the condition would resolve on its own. Patients might be recommended to take up pelvic floor exercises which help strengthen the muscles that control urination.
Overactive Bladder Causes
This condition may also take the form of urinary incontinence. The treatment then includes the use of medicines, medical devices to prevent urine leakage, therapies to improve the bladder muscles, or surgical procedures. The treatment plan for frequent or urgent urination is largely dependent on the cause.
These worries may increase your risk of anxiety and depression. While some people need to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, others have spasm or excess tension in the pelvic floor muscles that can make their overactive bladder worse. In this case, you can work with a pelvic floor physical therapist on relaxing and coordinating these muscles.
When to get help with urge incontinence and urgency
Do you find yourself having the urge to urinate as soon as you get home? Augmentation cystoplasty surgery to enlarge your bladder using tissue taken from your intestine. Medications or bladder botulin toxin injections (Botox®) to relax your bladder muscle so it can hold more urine. Drink less caffeinated and carbonated beverages and alcohol. These substances can irritate an overactive bladder. Leaking urine before you can make it to the bathroom or just after you peed.

For example, you may leak urine if you cough or sneeze, and also experience very intense urges to pass urine. Though it occurs more often as people get older, urinary incontinence isn't an inevitable consequence of aging. If urinary incontinence affects your daily activities, don't hesitate to see your doctor. For most people, simple lifestyle and dietary changes or medical care can treat symptoms of urinary incontinence. UTIs happen when bacteria or something else infects parts of your urinary system, which includes your bladder, urethra and kidneys.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, the average person should urinate somewhere between between six and eight times in a 24-hour period. While an individual is occasionally likely go more frequently than that, daily incidences of urinating more than eight times may signal a concern for too-frequent urination. Key in Lock syndrome is when you have a very strong urge to urinate and the bladder is unable to control holding liquid due to involuntary contractions.

The urinary system removes waste from the body through urine. The kidneys are located toward the back of the upper abdomen. They filter waste and fluid from the blood and produce urine. Urine moves from the kidneys through narrow tubes to the bladder.
The feeling went away for a while and then as I got closer to my exit, the urge to poop dropped on me like a ton of bricks. I suddenly was contemplating making a stop at the nearest gas station or bush, but I remained strong. As I pulled up to my house the urge was unbearable.
But untreated urge incontinence may get worse, and it could interfere with daily life activities and relationships. Another technique is to delay urination when the urge strikes. You may also try urinating and then going again immediately afterward to learn how to empty the bladder completely. Simply concentrating on your pelvic floor region and contracting will activate the correct muscles. Repeat this sequence for as many repetitions as you can, three or more times per day.
Nerves carry signals from your brain to your bladder and sphincter muscles. Nerve stimulators are small devices that resemble pacemakers. The permanent device, inserted under the skin of your abdomen, has a lead wire that hooks up to the sacral nerve. It sends light pulses to the nerve to help control your bladder’s functioning.

At first, you may go every hour and then increase the wait time by half-hour intervals until you can make it 3 to 4 hours without leakage. Adjust your lifestyle habits to be healthier overall. In addition, try to lose weight if you have overweight.
Some treatments can be self-administered at home. Talk to your doctor if your symptoms worsen or don’t improve. This plain film X-ray study can be used to diagnose conditions affecting the urinary and gastrointestinal systems. This tests the strength of your pelvic floor muscles. Your doctor can diagnose your specific type of incontinence and its cause, and they can suggest possible treatment options.

No comments:
Post a Comment